The Inductor Reactance Calculator is a tool to calculate the Reactance of the Inductor on one click. The reactance of an inductor is a key concept in electrical engineering and is used to describe the opposition that an inductor presents to alternating current (AC) flow. Reactance is a measure of how much the inductor resists the change in current due to the changing voltage across it.
Inductor Reactance Calculator
The reactance of an inductor (\(X_L\)) is calculated using the following formula:
\[ X_L = 2 \pi f L \]
Where:
\( X_L \) is the reactance of the inductor in ohms (\(\Omega\)).
\( \pi \) (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
\( f \) is the frequency of the AC signal in hertz (Hz).
\( L \) is the inductance of the inductor in henrys (H).
Key points to understand about inductor reactance:
1. Opposition to AC:
An inductor stores energy in its magnetic field when current flows through it. When the current changes in response to an AC voltage, the magnetic field also changes, generating an opposing voltage that resists the current change. This opposition is known as reactance.
2. Dependence on Frequency:
The reactance of an inductor increases with higher frequencies. This means that inductors have a greater opposition to rapid changes in current (high-frequency AC) compared to low-frequency AC.
3. Units:
The units of reactance are ohms (\(\Omega\)), which is the same unit used for resistance. However, reactance specifically applies to AC circuits, while resistance applies to both AC and DC circuits.
4. Relationship with Inductance:
Inductance (\(L\)) is a property of the inductor that determines how effectively it stores energy in its magnetic field. The greater the inductance, the higher the reactance for a given frequency.
5. Phase Shift:
Reactance also introduces a phase shift between voltage and current in AC circuits. The phase shift is 90 degrees in an ideal inductor, meaning the current lags behind the voltage.
6. Reactance Triangle:
Reactance, resistance, and impedance (a complex combination of resistance and reactance) can be represented using a right triangle, known as the “impedance triangle.”
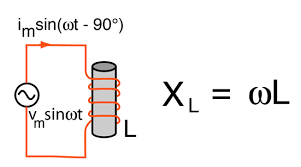
In summary, the reactance of an inductor quantifies its opposition to changes in AC current due to changing voltages. It’s calculated using the formula \(X_L = 2 \pi f L\) and is influenced by both the frequency of the AC signal and the inductor’s inductance.
Thanks for reading the post Inductor Reactance Calculator.
Read: