Linear Induction Motor (LIM) is a category of electric motor that is designed to provide linear motion, as opposed to the traditional rotational motion of conventional motors. They find application in various industries where linear movement is required, offering advantages such as simplicity, reliability, and high efficiency.
What is a Linear Induction Motor?
A Linear Induction Motor (LIM) is an electric motor that produces linear motion directly without the need for any intermediate mechanical conversion. Just like a traditional rotating induction motor, a linear induction motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the interaction between a magnetic field and current generates movement. LIMs find applications in various transportation systems, manufacturing processes, and other scenarios that demand precise linear motion.
Types of Linear Induction Motor
There are two main types of Linear Induction Motors:
- Open-Loop LIM: In this configuration, the motor operates without feedback control. It is relatively simple and is suitable for applications where high precision is not essential.
- Closed-Loop LIM: This type of LIM incorporates position feedback and control mechanisms to achieve higher precision in motion control. Closed-loop LIMs are used in applications that require accurate positioning and speed control.
Theory
The theory behind Linear Induction Motors is rooted in electromagnetic induction. When alternating current passes through a primary winding, it generates a varying magnetic field. This varying magnetic field induces eddy currents in a secondary conductor, leading to a magnetic interaction that propels the secondary component linearly.
Working Principle
The working principle of a Linear Induction Motor involves the interaction of magnetic fields and induced currents. The motor consists of a primary winding (stator) and a secondary conductor (slider). As alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a moving magnetic field. This moving magnetic field induces currents in the secondary conductor, generating a force that propels the slider along the length of the motor.
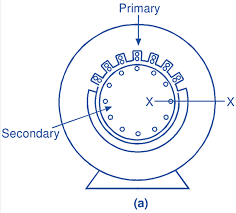
Construction
A Linear Induction Motor’s construction is quite distinct from traditional rotary motors. It typically consists of a primary winding arrangement and a secondary conductor. The primary winding is typically energized with a three-phase AC supply, and the secondary conductor can take various forms, such as a flat plate or a cylindrical rod.
Application of Linear Induction Motor
Linear Induction Motors have a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Transportation Systems: LIMs are used in high-speed trains, people movers, and even roller coasters, where the linear motion provides efficient and smooth movement.
- Material Handling: They are employed in conveyors, escalators, and automated warehouses to transport goods and materials.
- Manufacturing: LIMs find application in assembly lines, machine tools, and automated production processes.
Speed Control of Linear Induction Motor
The speed of a Linear Induction Motor can be controlled using various techniques such as varying the frequency of the applied AC supply, adjusting the voltage, or utilizing sophisticated control systems like pulse width modulation (PWM). The choice of control method depends on the specific application and desired performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Linear Induction Motor
Advantages:
- Direct linear motion without the need for mechanical components like gears or pulleys.
- High efficiency and reliability due to fewer moving parts.
- Suitable for harsh environments and high-temperature conditions.
- Minimal maintenance requirements.
Disadvantages:
- Complex control systems required for precise motion control.
- Limited to applications requiring linear motion.
In conclusion, the Linear Induction Motor is a versatile and efficient solution for applications requiring linear motion. Its working principle, construction, and applications make it an intriguing technology with significant potential in various industries. With advancements in control systems and technology, the Linear Induction Motor continues to revolutionize transportation, manufacturing, and automation processes.
Read: Impedance of Inductor