The Thermal Noise Calculator is a tool to calculate the thermal noise. Thermal noise is also known as Johnson-Nyquist noise. It is a type of random electrical noise that exists in electronic circuits and components due to the thermal agitation of charge carriers (such as electrons) within conductors. It is an intrinsic property of all conductors at non-zero temperatures and is independent of the signal passing through the circuit.
Thermal Noise Calculator
| Temperature (T) in Kelvin | Resistance (R) in Ohms | Bandwidth (B) in Hertz |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Noise Voltage (Vn) in Micro-Volts | ||
The thermal noise arises from the random thermal motion of charge carriers within the conductors, leading to random fluctuations in voltage and current. This noise manifests itself as small, random variations in the electrical signals present in the circuit.
The above calculator works on following formula:
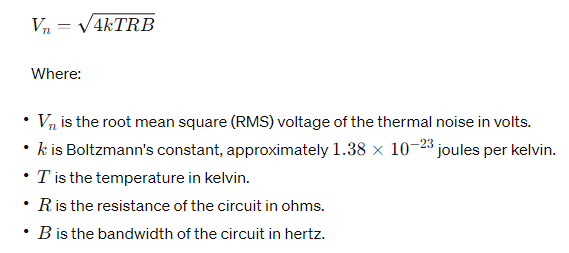
Thermal noise is proportional to the temperature of the conductor, the resistance of the conductor, and the bandwidth of the electrical signal passing through the circuit. It is characterized by a Gaussian (or normal) distribution and has a flat power spectral density across a wide range of frequencies.
In practical electronic circuits, thermal noise can have significant effects, particularly in low-noise applications where high precision and sensitivity are required. It sets a fundamental limit on the smallest signals that can be reliably detected or measured in electronic systems. Measures to mitigate thermal noise include reducing the operating temperature of the circuit (such as through cooling methods) and minimizing the resistance of conductors in critical signal paths.