Which Reactant in the Photosynthesis Equation is the Source of Hydrogen for Sugar Molecules? The answer to this question is “Water”.
In the photosynthesis equation, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the source of carbon, and water (H2O) is the source of hydrogen for sugar molecules. During the process of photosynthesis, plants, and other photosynthetic organisms use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (sugar) and oxygen. The hydrogen atoms from water molecules are incorporated into the sugar molecules, while oxygen is released as a byproduct.
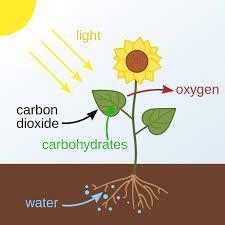
Balanced Photosynthesis Equation
The balanced equation for photosynthesis is:
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2
Here, carbon dioxide provides the carbon atoms for building glucose molecules, and water provides the hydrogen atoms that are used to form the hydrogen component of glucose.
The Process of Photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis in plants is a complex series of chemical reactions that occur in the chloroplasts. These reactions allow plants to capture light energy from the sun and convert it into energy-rich molecules, primarily glucose (sugar), which serves as a source of energy for the plant’s growth and other metabolic processes. Here’s a detailed explanation of the process:
- Light Absorption: Photosynthesis begins when chlorophyll and other pigments in the chloroplasts absorb sunlight. These pigments are found in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts, which are specialized structures designed to capture light energy.
- Light-Dependent Reactions: These reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes. The absorbed light energy is used to power a series of complex reactions that generate two important molecules: ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These molecules temporarily store the captured light energy.During these reactions, water molecules are split through a process called photolysis. This splitting of water releases oxygen gas (O2) as a byproduct. The oxygen is either used by the plant or released into the atmosphere.
- Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions): The ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions are then used in the Calvin cycle, which takes place in the stroma (the fluid-filled space) of the chloroplasts.The Calvin cycle is also known as the “dark reactions” or “carbon fixation” because they don’t directly require light. In this cycle, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is combined with the hydrogen atoms from NADPH to create glucose and other organic molecules. The cycle involves a series of enzymatic reactions that rearrange and transform the carbon atoms into sugars.
- Glucose Production: The end product of photosynthesis is glucose (C6H12O6). Glucose is a complex sugar that stores a substantial amount of energy in its chemical bonds. Plants use glucose as an immediate source of energy for cellular activities, and any excess glucose is stored as starch for later use.
- Release of Oxygen: The oxygen produced during the light-dependent reactions is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct. This oxygen is vital for the respiration of both plants and animals, as well as for the overall oxygen balance on Earth.
In summary, photosynthesis is a multi-step process in which plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process not only sustains the plants themselves but also plays a critical role in maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere and supporting life on the planet.
Thanks for reading the blog Which Reactant in the Photosynthesis Equation is the Source of Hydrogen for Sugar Molecules?
Read: